10 most important typescript concepts
Introduction#
TypeScript is an open-source programming language that is a superset of JavaScript. It adds optional static typing and class-based object-oriented programming to the language. As a result, TypeScript is becoming increasingly popular among developers, especially those working with large-scale projects. In this blog post, we will discuss 10 of the most important TypeScript concepts that every developer should know.

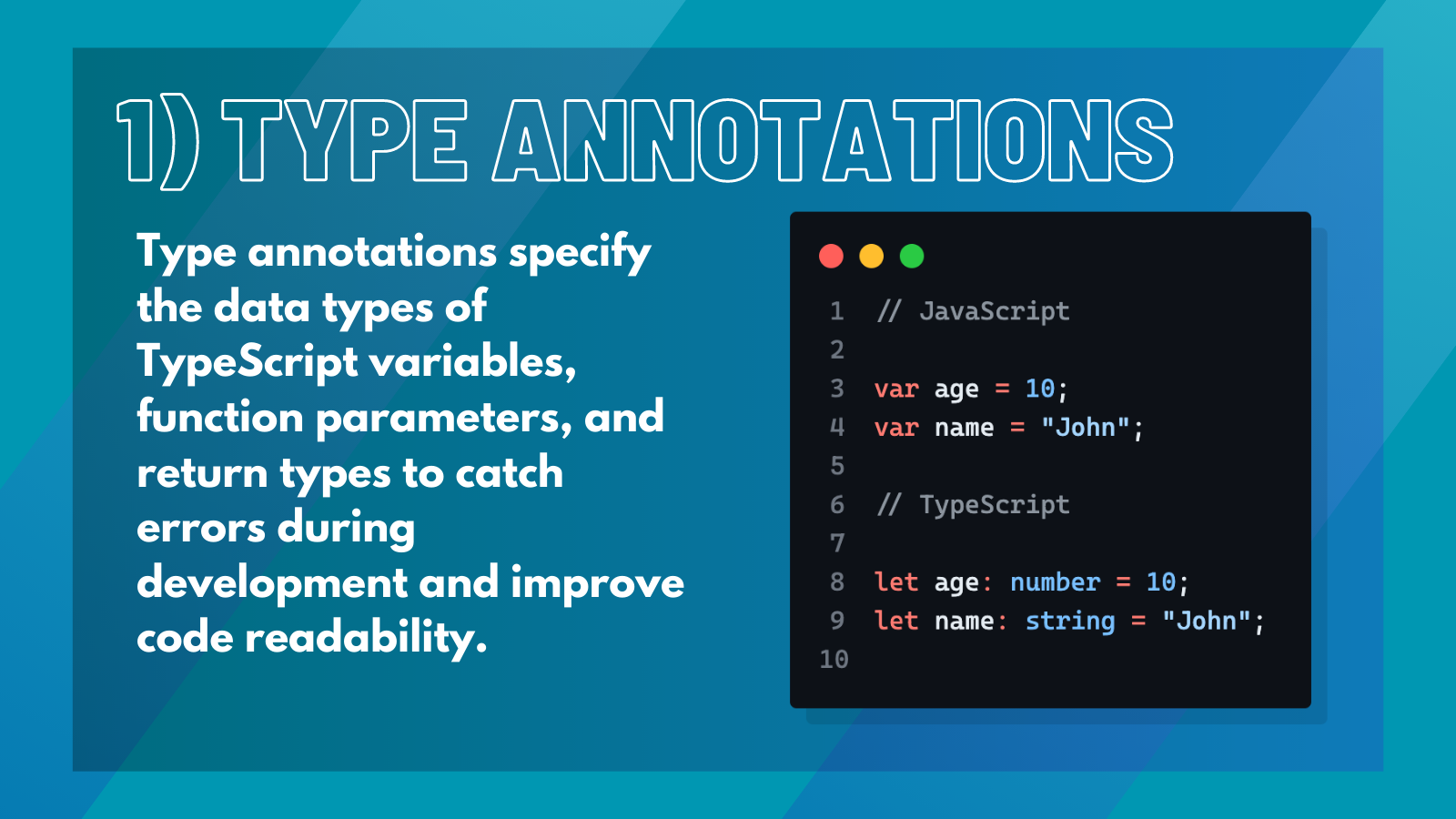
1. Type Annotations#
Type annotations are a crucial concept in TypeScript. They allow developers to specify the data types of variables, function parameters, and return types. This can help catch errors during development and improve code readability.
For example,
This specifies that the variable age should be of type number and have an initial value of 27.
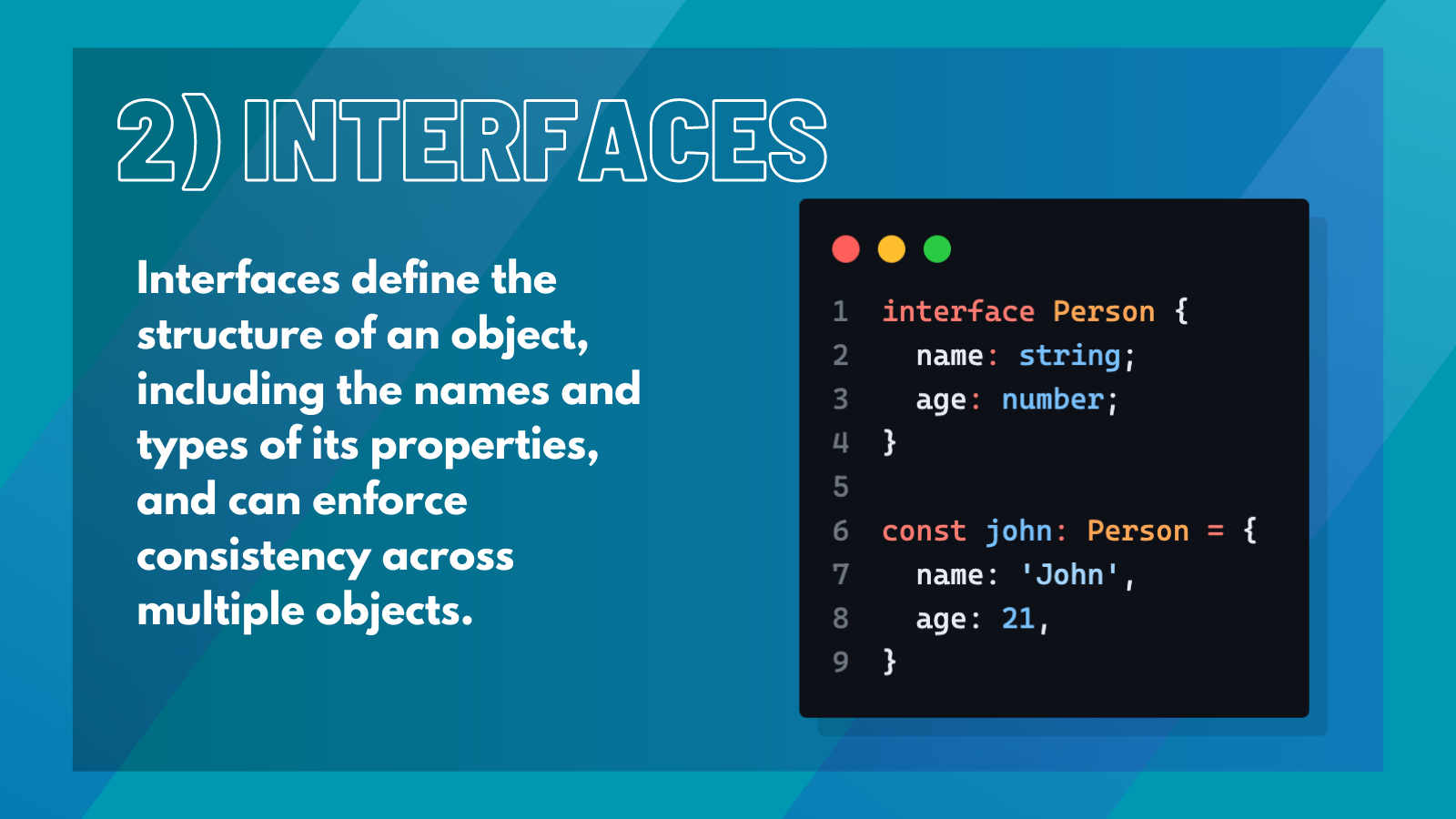
2. Interfaces#
Interfaces are used to define the structure of an object. They specify the names and types of the object's properties and can be used to enforce consistency across multiple objects.
For instance,
This defines an interface for a Person object with a name property of type string and an age property of type number.
3. Classes#
Classes are a core concept in object-oriented programming, and TypeScript has full support for them. Classes allow developers to define blueprints for objects that share the same properties and methods. They can also include constructors, access modifiers, and inheritance.
For example,
This defines a Animal class with a name property and a constructor that sets the name property.

4. Generics#
Generics are a powerful feature in TypeScript that allow for the creation of reusable code. They allow developers to create functions and classes that can work with a variety of data types.
For example,
This defines a generic identity function that returns the same value that is passed to it.

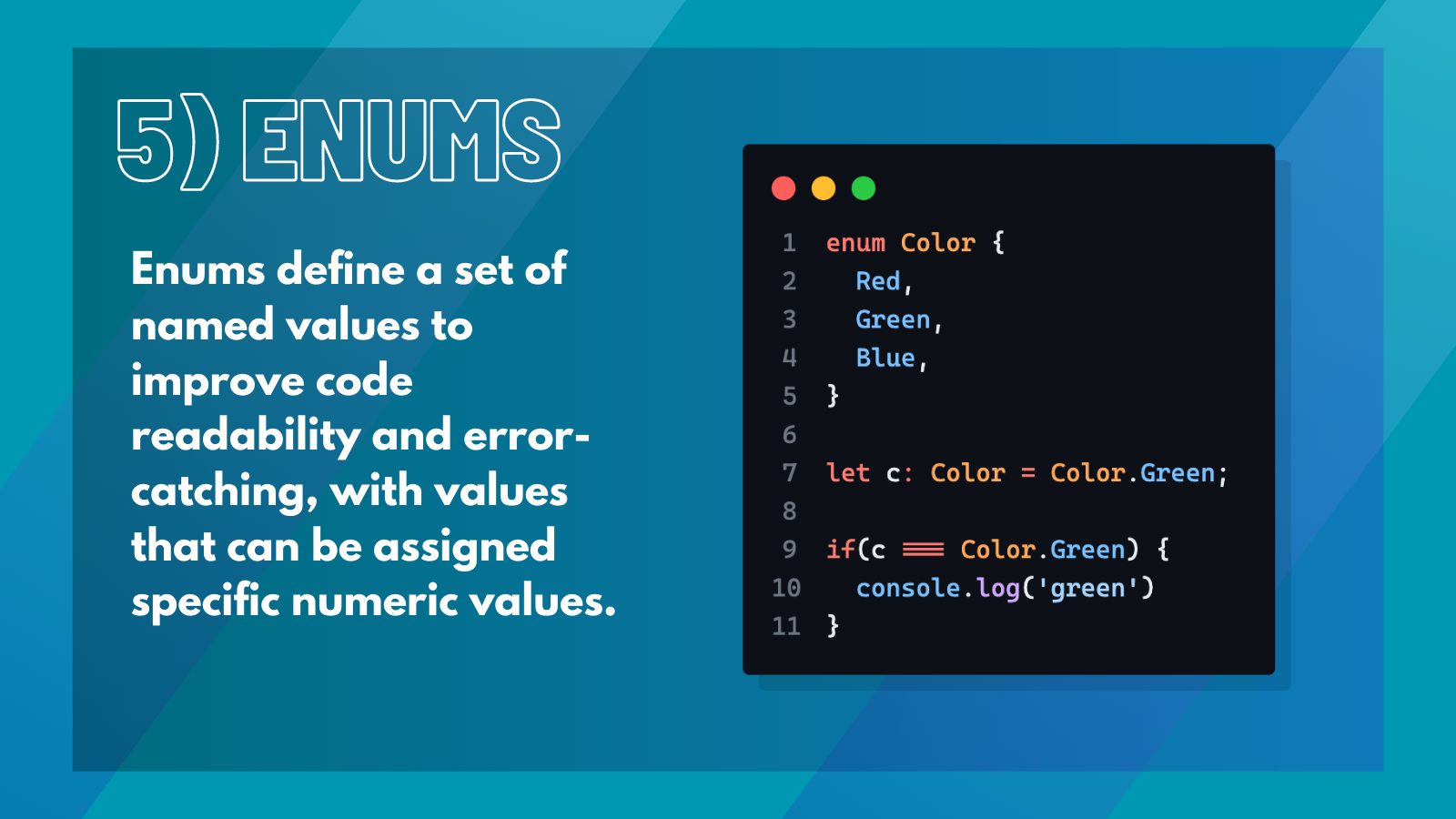
5. Enums#
Enums are a way to define a set of named values. They can improve code readability and help catch errors.
For instance,
This defines an Color enum with three named values: Red, Green, and Blue. Enum values can also be assigned specific numeric values, such as:
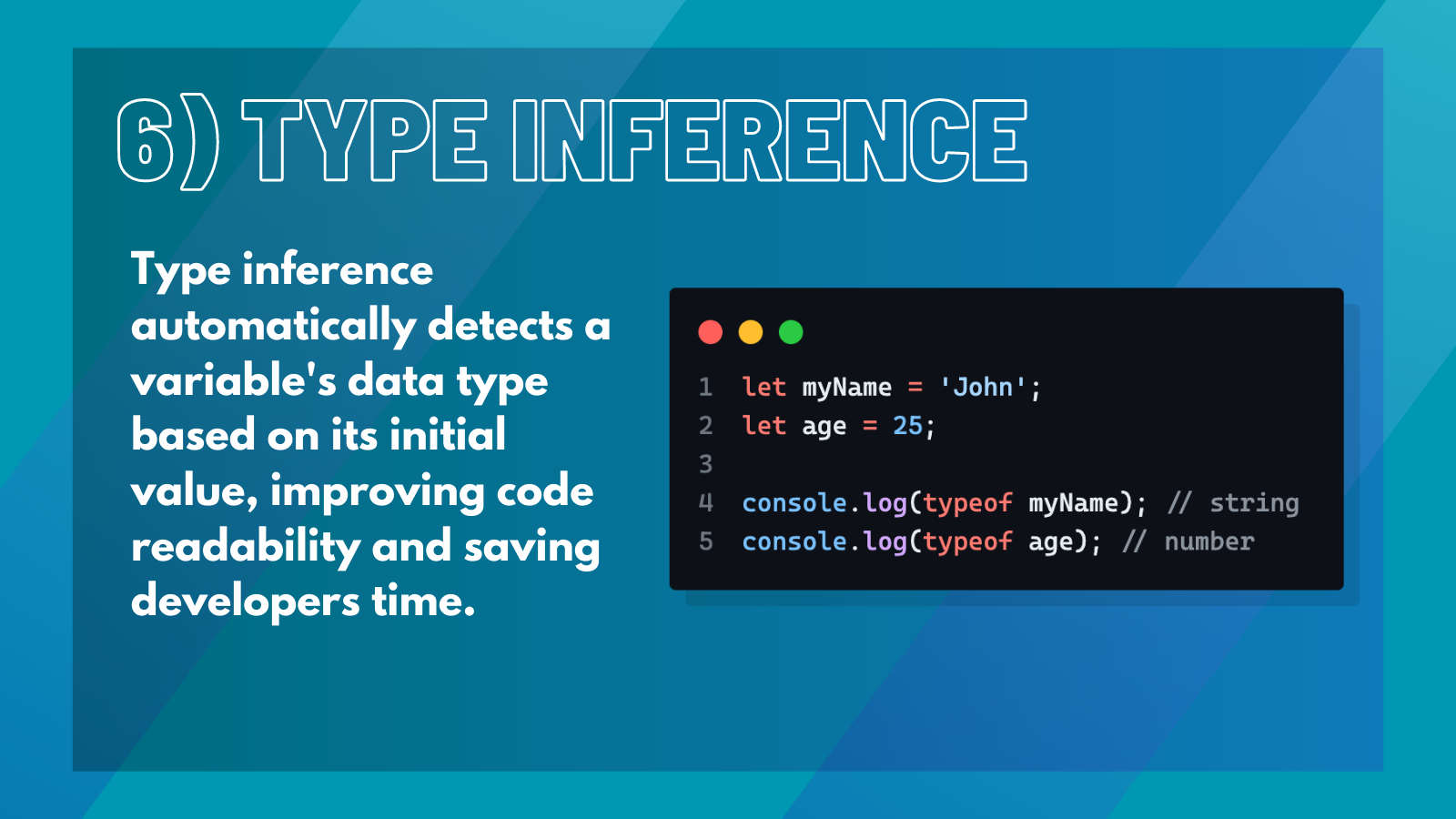
6. Type Inference#
Type inference is a feature of TypeScript that allows developers to omit type annotations in certain situations.
For example,
This will automatically be inferred as a number type because it is assigned a numeric value. Type inference can also be used with function parameters and return types, such as:
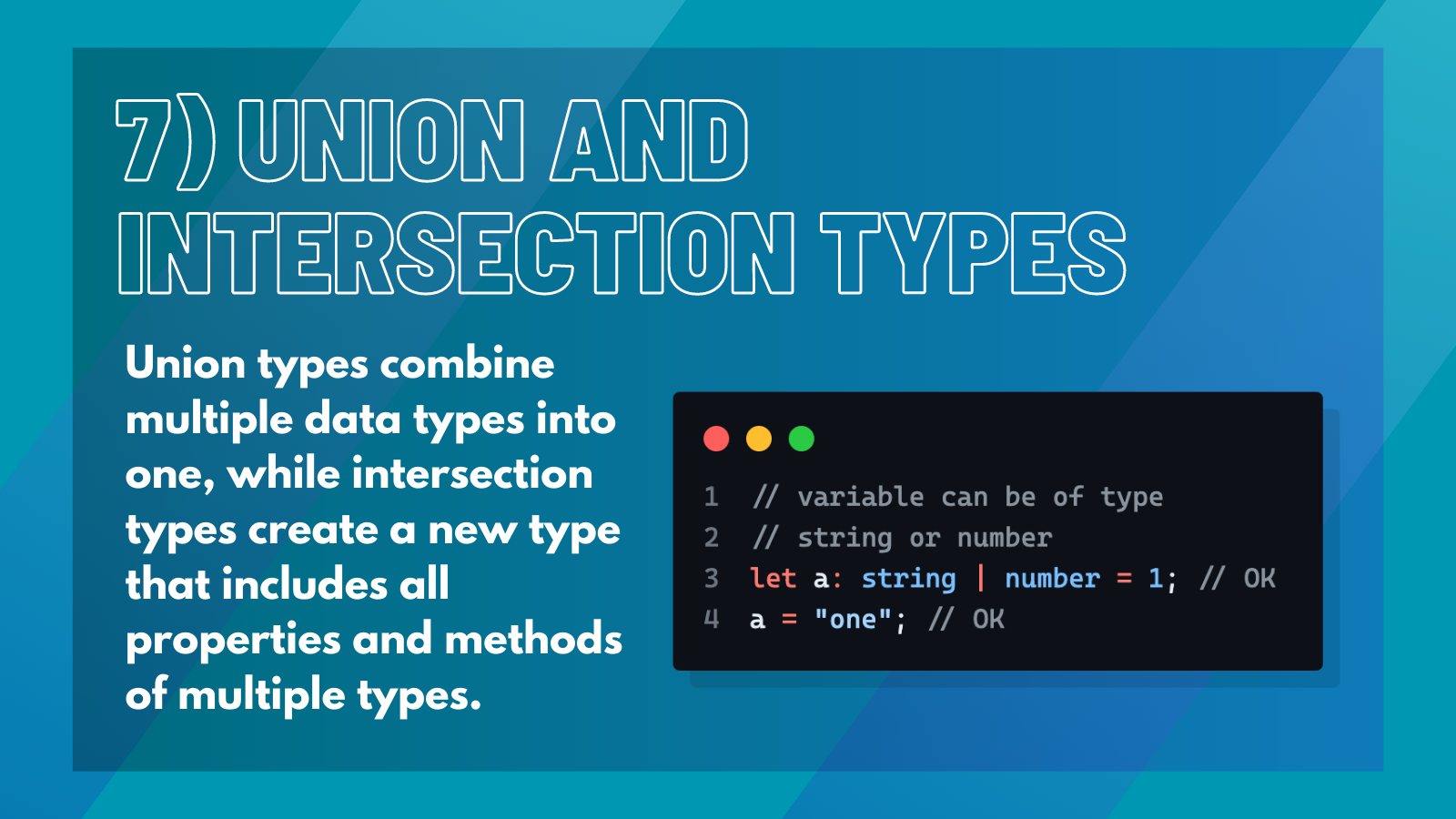
7. Union and Intersection Types#
Union types allow for the combination of two or more data types into one. This can be useful when a function or variable can accept multiple types of data.
For example,
This specifies that the age variable can be of type number or string. Intersection types, on the other hand, allow for the creation of a new type that includes all properties and methods of multiple types.
For example,
This creates a new type Animal that has all properties and methods of both the Dog and Cat types.
8. Type Guards#
Type guards are a feature in TypeScript that allow developers to check the type of a variable at runtime. This can be useful when working with union types or other situations where the type of a variable may not be known.
For instance,
This checks if the age variable is of type number before performing a multiplication operation.

9. Decorators#
Decorators are a feature in TypeScript that allow for the addition of metadata to classes, methods, and properties. They can be used to modify the behavior of a class or to provide additional information for tools like code analyzers.
For example,
This marks the MyClass class as deprecated and will generate a warning when used.

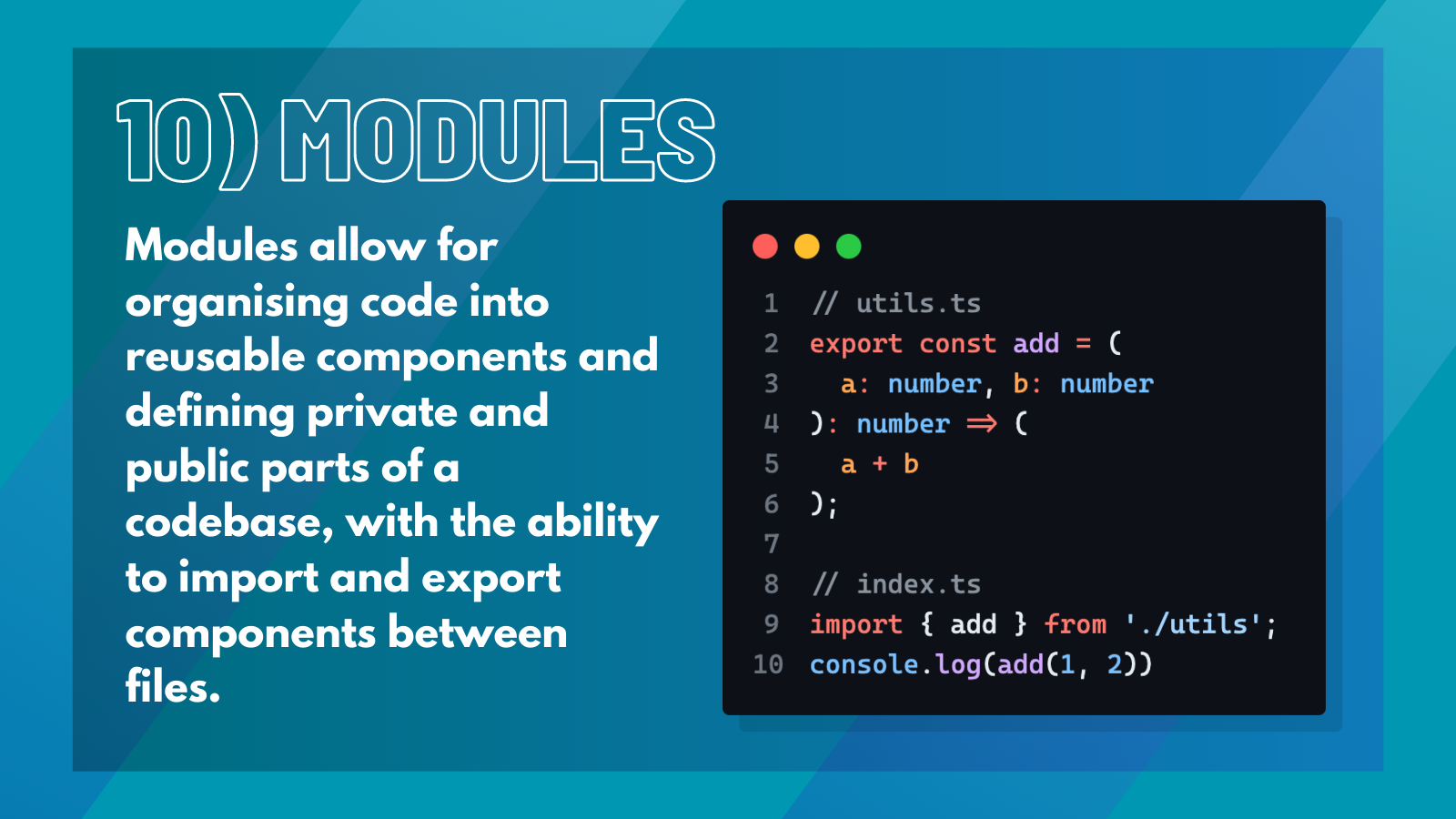
10. Modules#
Modules are a way to organize code into smaller, reusable components. They allow developers to define private and public parts of a codebase and to import and export components between files.
For example,
This exports the MyClass class from a module, while:
This imports the MyClass class into another module.
Conclusion#
TypeScript is a powerful language that is becoming increasingly popular among developers. By mastering these 10 important concepts, developers can write more efficient and maintainable code. While there are many other concepts and features in TypeScript, these 10 are a great starting point for any developer looking to learn the language.